To reference this electronic educational resource according to the APA style for Web references, use:
Liem EB (2006): Combitube Intubation. Retrieved <insert date of retrieval here>, from University of Florida Department of Anesthesiology, Center for Simulation, Advanced Learning and Technology, Virtual Anesthesia Machine Web site: http://vam.anest.ufl.edu/airwaydevice/combitube/index.html
Keywords: Combitube, Intubation, difficult airway, airway management
Esophageal-Tracheal- Combitube (ETC), Kendall-Sheridan Corporation
Introduction
The Combitube is a twin lumen device designed for use in emergency situations and difficult airways. It can be inserted without the need for visualization into the oropharynx, and usually enters the esophagus. It has a low volume inflatable distal cuff and a much larger proximal cuff designed to occlude the oro- and nasopharynx (1-4).
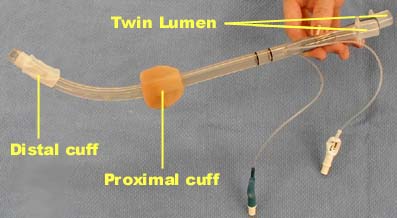
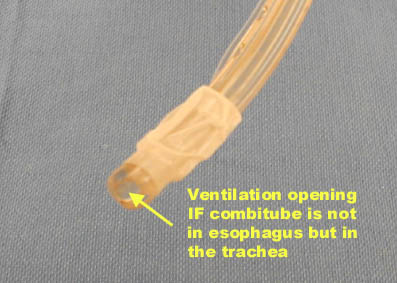
If the tube has entered the trachea, ventilation is achieved through the distal lumen as with a standard ETT. More commonly the device enters the esophagus and ventilation is achieved through multiple proximal apertures situated above the distal cuff. In the latter case the proximal and distal cuffs have to be inflated to prevent air from escaping through the esophagus or back out of the oro- and nasopharynx.
|
|
||
The Combitube has been used effectively in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (11,14,15). It has been used succesfully in patients with difficult airways secondary to severe facial burns, trauma, upper airway bleeding and vomiting where there was an inability to visualize the vocal cords (9,10,12,13). It can be used in patients whose cervical spine has been immobilized with a rigid cervical collar, though placement may be more difficult(1,7). Ventilation does not seem to be affected by the rigid cervical collar if the Combitube can be placed (6).
The Combitube can only be used in the adult population as no pediatric sizes are available.
Complications of the Combitube include an increased incidence of sore throat, dysphagia and upper airway hematoma when compared to endotracheal intubation and LMA(16). Esophageal rupture is a rare complication but has been described (20-23). Known esophageal disease is a contra-indication to the use of the Combitube. These complications may be partially preventable by avoiding over-inflation of the distal and proximal cuffs (see recommendations below). Compared to intubation with an endotracheal tube under direct laryngoscopy or using the LMA, the Combitube seems to exert a more pronounced hemodynamic stress response (17,18).
Although it is possible to maintain an airway with the Combitube, endotracheal intubation is the preferred method for definitively securing the airway. Either the oral or the nasal route can be used for fiberoptic-guided airway exchange. The Combitube is left in place and the proximal cuff is partially deflated for fiber-optic intubation with an endotracheal tube (19,24).
Preparation
Little preparation is needed beyond testing both cuffs
for leaks. The pilot balloon of the distal cuff is white and is marked
with the number 2. Test the distal cuff by inflating with 15 ml of
air. The pilot balloon of the proximal cuff is blue and is marked
with the number 1. Test the proximal cuff by inflating with 85 ml
of air.
The available sizes are 41 Fr and 37 Fr. The original recommendation
by the manufacturer is to use 41 Fr for patients taller than 5ft (152
cm) and 37 Fr for patients below that height. However, the bulky design
of the 41 Fr can make it more technically difficult to insert and
some authors (3) have reported satisfactory results using the 37 Fr
Combitube on taller patients. A redesigned Combitube has been described
by creating an enlarged hole in the pharyngeal lumen that allows fiberoptic
access, tracheal suctioning, and tube exchange over a guide wire (8).
However, this type of Combitube is not available in our department.
Oral Intubation: A Step by Step Guide
The combitube can be inserted blindly without the aid of a laryngoscope. However, use of a laryngoscope has been reported to facilitate placement of the Combitube. It appears that the laryngoscope aids insertion by forcefully creating a greater space in the hypopharynx.
- Induce patient as if for regular intubation.
- Patient head position can be neutral.
- When direct laryngoscopy is attempted and the vocal cords
can be visualized, the Combitube should be placed in the trachea
and used as a regular endotracheal tube.
- Inflate the distal cuff with just enough air until no leak is present.
- Check for bilateral breath sounds over the lungs and confirm endotracheal placement on the capnogram.
- Connect the breathing circuit to the white connector number 2.
- If the Combitube is placed blindly, the left hand should
elevate the chin while the right hand maneuvers the Combitube.
Alternatively, more space can be created in the hypopharynx
by using a laryngoscope with the left hand. The Combitube should
be inserted to such a depth that the upper incisors are between
the two black guidelines on the external surface of the tube
:
- Inflate the distal cuff with 12 ml.
- Ventilate through the white connector number 2 and listen for gurgling sounds over the epigastrium or breath sounds over the lungs. If breath sounds are heard over the lungs the Combitube has been placed in the trachea and can be used as a regular ETT as described above after confirmation on the capnogram. If gurgling sounds are heard over the epigastrium, the Combitube is located in the esophagus.
- Inflate the proximal cuff with just enough air until either no leak is present or a subjective sensation of increased resistance to cuff inflation is encountered. This is usually achieved by inflating with 50-75 ml of air. This is less than the 85 ml recommended by the manufacturer but has been found to cause less upper airway trauma (1)
- Ventilate through the blue connector number 1, listen for breath sounds over the lungs and confirm ventilation on the capnogram.
Troubleshooting Tips
Unable to ventilate patient through blue connector number 1
Make sure the Combitube is not per chance in the trachea. Attempt to ventilate through connector number 2, if breath sounds are heard over the lungs then the combitube has been placed in the trachea instead of the esophagus. Deflate the large proximal pharyngeal cuff and use the Combitube as a regular ETT.
Unable to ventilate patient through either connector
Confirm that the combitube has been placed in the esophagus by listening for epigastric gurgling sounds while ventilating through connector number 2. Then withdraw the combitube 2-3 cm at a time while ventilating through connector number 1 until breath sounds are heard over the lungs. The most common cause of this inability to ventilate to ventilate through either connector is an excessive insertion depth of the combitube (relative to the patient). This will cause obstruction of the glottic opening by the large proximal pharyngeal cuff (1,5).
Webauthor: E.B.Liem
Consultants: D.Gravenstein
Contributor: T.L. Euliano
- Mercer MH, Gabbott DA. Insertion of the Combitube airway with the cervical spine immobilised in a rigid cervical collar. Anaesthesia. 1998 Oct;53(10):971-4.
- Bishop MJ, Kharasch ED. Is the Combitube a useful emergency airway device for anesthesiologists? Anesth Analg. 1998 May;86(5):1141-2.
- Walz R, Davis S, Panning B. Is the Combitube a useful emergency airway device for anesthesiologists? Anesth Analg. 1999 Jan;88(1):233.
- Urtubia R, Aguila C. Combitube: a new proposal for a confusing nomenclature. Anesth Analg. 1999 Sep;89(3):803.
- Green KS, Beger TH. Proper use of the Combitube. Anesthesiology. 1994 Aug;81(2):513-4
- Mercer MH, Gabbott DA. The influence of neck position on ventilation using the Combitube airway. Anaesthesia. 1998 Feb;53(2):146-50.
- Gwinnutt CL, Kishen R. The Combitube and cervical spine immobilisation. Anaesthesia. 1999 Mar;54(3):304-5.
- Krafft P, Roggla M, Fridrich P, Locker GJ, Frass M, Benumof JL. Bronchoscopy via a redesigned Combitube in the esophageal position. A clinical evaluation. Anesthesiology. 1997 May;86(5):1041-5.
- Wagner A, Roeggla M, Roeggla G, Weiss K, Marosi C, Locker GJ, Knapp S, Staudinger T, Metnitz PG, Frass M. Emergency intubation with the combitube in a case of severe facial burn. Am J Emerg Med. 1995 Nov;13(6):681-3.
- Staudinger T, Tesinsky P, Klappacher G, Brugger S, Rintelen C, Locker G, Weiss K, Frass M. Emergency intubation with the Combitube in two cases of difficult airway management. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1995 Mar;12(2):189-93.
- Staudinger T, Brugger S, Watschinger B, Roggla M, Dielacher C, Lobl T, Fink D, Klauser R, Frass M. Emergency intubation with the Combitube: comparison with the endotracheal airway. Ann Emerg Med. 1993 Oct;22(10):1573-5.
- Eichinger S, Schreiber W, Heinz T, Kier P, Dufek V, Goldin M, Leithner C, Frass M. Airway management in a case of neck impalement: use of the oesophageal tracheal combitube airway. Br J Anaesth. 1992 May;68(5):534-5.
- Klauser R, Roggla G, Pidlich J, Leithner C, Frass M. Massive upper airway bleeding after thrombolytic therapy: successful airway management with the Combitube. Ann Emerg Med. 1992 Apr;21(4):431-3.
- Frass M, Frenzer R, Rauscha F, Schuster E, Glogar D. Ventilation with the esophageal tracheal combitube in cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Promptness and effectiveness. Chest. 1988 Apr;93(4):781-4.
- Frass M, Frenzer R, Rauscha F, Weber H, Pacher R, Leithner C. Evaluation of esophageal tracheal combitube in cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Crit Care Med. 1987 Jun;15(6):609-11.
- Oczenski W, Krenn H, Dahaba AA, Binder M, El-Schahawi-Kienzl I, Kohout S, Schwarz S, Fitzgerald RD. Complications following the use of the Combitube, tracheal tube and laryngeal mask airway. Anaesthesia. 1999 Dec;54(12):1161-5.
- Panning B, Sterz F. Hemodynamic and catecholamine stress responses to insertion of the Combitube, laryngeal mask airway or tracheal intubation. Anesth Analg. 2000 Jan;90(1):231-2.
- Oczenski W, Krenn H, Dahaba AA, Binder M, El-Schahawi-Kienzl I, Jellinek H, Schwarz S, Fitzgerald RD. Hemodynamic and catecholamine stress responses to insertion of the Combitube, laryngeal mask airway or tracheal intubation. Anesth Analg. 1999 Jun;88(6):1389-94.
- Gaitini LA, Vaida SJ, Somri M, Fradis M, Ben-David B. Fiberoptic-guided airway exchange of the esophageal-tracheal Combitube in spontaneously breathing versus mechanically ventilated patients. Anesth Analg. 1999 Jan;88(1):193-6.
- Klein H, Williamson M, Sue-Ling HM, Vucevic M, Quinn AC. Esophageal rupture associated with the use of the Combitube. Anesth Analg. 1997 Oct;85(4):937-9.
- Krafft P, Nikolic A, Frass M. Esophageal rupture associated with the use of the Combitube. Anesth Analg. 1998 Dec;87(6):1457.
- Walz R, Bund M, Meier PN, Panning B. Esophageal rupture associated with the use of the Combitube. Anesth Analg. 1998 Jul;87(1):228.
- Tanigawa K, Shigematsu A. Choice of airway devices for 12,020 cases of nontraumatic cardiac arrest in Japan. Prehosp Emerg Care. 1998 Apr-Jun;2(2):96-100.
- Ovassapian A, Lui S, Krejcie T. Fiberoptic tracheal intubation with Combitube in place. Anesth Analg 1993;76;S1-476.